Activating the potential of healing
- The Skin
“““““““`
1-1. The epidermis
Point location: the needle is inserting onto the epidermis
Depth: range of 0.07- 0.12 cm
Response: no pain or bleeding, the skin shows red in color and the skin feel worm
After needle: Chinese coin gentle scratches or/and moxa heat the point
Physiology:
Skin consists have epidermis stem cells in the basal layer are ensured the process of epidermal renewal.
The deepest layer of the epidermis is the stratum basal or the stratum germinativum in this layer the cells with clear cytoplasm, which are dendritic cells of the immune system and sensory system.
Results: activated the epidermis cells can improve wound healing and renewal the skin on the face.
1-2. Insertion into dermis
“““““““““““““`
Location: two layers—papillae and reticular
Needling depth: depth 0.5cm-0.6cm and 1.3cm length needle is often used
Response: stimulated the receptors and increases stretching power
Needle diameter: small diameter is for gentle stimulation
In the case of SCI a correct needle insertion method: the large diameter needle stimulation should be large enough to activated the action potential regenerate the nerve impulses that will rebuild the sensory neuron and motor neuron connection and function. The matter is the needle stimulation must be strong!
Repetitive needle techniques are provided.
Location of sensitive points
“““““““““““““““““
* ACU points—Jing Well points K1 GV26 sensitive points are selected
* Neurological sensitive receptors– Merkel’s discs—tactile domes are found in hairless skin, such as the fingertips.
Meissner’s corpuscles are located in the dermal papillae of the skin especially palm of the hand and plantar of the foot, nipple and external genitalia.
* Dorsal ganglia: The cell nuclei of somatic sensory and afferent fibers lie in ganglia throughout the spine. These neurons are responsible for relaying information about the body to the central nervous system.
* Treating paraplegic limp requires select sensitive points and correct needle insertion method is applies large diameter needle fast and repetitively (four times is a second) repeat inserted into a point.
- Activated The Stem Cells
““““““““““““““““““
Acupuncture is activated those stem cell from one’s own body-autologous must be able to produce new blood cells and immune cells over a period of term, demonstrating potency.
1-1 Endothelial cells
““““““““““`
Point Location: At surrounding the wound side
Method: the needle is inserted perpendicularly into the skin deep into the subcutaneous and the side of the muscles: after needling scratches the points
Physiology:
That can reduces the tension of the skin improves blood circulation and form new blood vessel to that region improves wound-healing processes.
1-2 Stem cells from lipid cells
““““““““““““““““`
Point Location: in subcutaneous and connective tissues ACU point ST25 or GB30 for example
Method: makes a straight line cross the rectus abdominis muscle for example; the points are on the line 1cm interval, inserting needle perpendicularly deep into the adipose tissues lifting and thrusting needle in the point 10 times after needling deep massages or deep scratches the points.
Physiology:
Adipose tissue (lipid cells) can produce stem cells. In body different part has adipose tissues
1-3 Bone marrow stem cells
“““““““““““““““`
Point Location: in periosteum to bone ACU point St31 or GB28 for example
Method: The tip of the sharp inserted deep into the big bone: such as iliac crest applies repetitive 10 times lifting and thrusting needling method deeper into the periosteum and bone massages and scratching the point.
Physiology:
The stimulation and drilling into the bone may produces stem cells and following the blood distributed into the blood circulation for wound healing especially for treating fracture healing in SCI
1-4 “Fire Burning the Mountain”
Pure Reinforcement Techniques
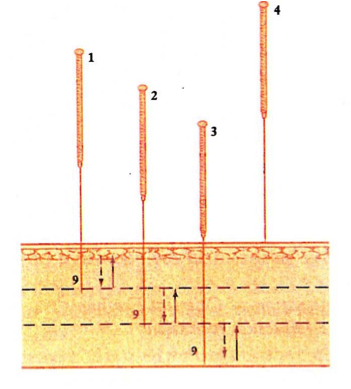
‘Fire Burning the Mountain’
METHOD:
The depth of the point is determined and mentally divided into three levels: Heaven, Man and Earth (Skin, Muscles and Periosteum). The Needle is slowly inserted through the skin, thrust firmly into the first level and lifted gently back to just under the skin. At each of the three levels, the needle is firmly thrust and lifted gently back to just beneath the skin. At each of the three levels, the needle is firmly thrust and gently lifted nine times. On completion, the needle is quickly withdrawn from the third (deepest) and the point sealed with the fingers.
If correctly applied, the patient feels a warm sensation at the local areas. If this is not so, the entire procedure may be repeated, but not more than three times, before the needle is completely withdrawn.
Needle insertion and stretching exercises activated the neurotrophin and neurotrofic factors improve the sensory neurons recovery and the motor neurons innervated into the muscles improve the muscles strength.
This needle technique is frequently applies for ACU treatment for long times and regards can reinforce the healing process it seems is work on activated the stem cells function.
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““
- Fire two gates—produce nerve impulses-neurotransmitters
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““`
1-1. ACU treatment is through needle techniques stimulation to the skin receptors and the muscles spindle fire the sensory neurons the first step is regain the sensory neurons function.
A gentle needling into the skin receptors not of necessity can produce action potential-nerve impulses, especially in the case of SCI, because the skin is lost sensation. If a strong needling method, which is strong enough depolarization in the postsynaptic membrane sufficient to reach the threshold then action potential- nerve impulses may produce as such a repetitive needle technique or hypersensitive point. The action potential- nerve impulses required get through the synapses processes, which are via the chemical channel, produce electronic nerve impulses-neurotransmitters transmitted to other neurons.
1-2. Types of motor neurons are Alpha motor neurons, beta motor neurons and gama motor neuron
“A single motor neuron may innervate many muscle fibers and a muscle fiber can undergo many action potential in the time taken for a single muscle twitch (faciculation). As a result, if an action potential arrives before a twitch has completed, the twitches can superimpose on one another, either through summation or tetanus.
In summation, the muscle is stimulated repetitively such that additional action potentials coming from the somatic nervous system arrive before the end of the twitch. The twitches thus superimpose on one another, leading to a force greater than that of a single twitch. On the other hand, tetanus is caused by constant, very high frequency stimulation – the action potentials come at such a rapid rate, which individual twitches are indistinguishable, and tension rises smoothly eventually reaching plateous.”
- The reflexes circulate
“““““““““““““““`
1-1. Initiate the needle stimulated receptors fire sensory neurons through neurotransmitters interneuron connects to motor neurons in spinal cord gray column
1-2. The sensory neurons ascending to central motor nuclei via descending tracts effect to inter-neurons and motor neurons
1-3. The nerves innervated to the muscles through origin of the muscle down to the insertion of the muscle for example: normally rectus abdomini from T7 to T12, when SCI lesion to T7 the muscles origin down to insertion T12 lost skin sensation and muscles movement; when the skin sensation return nerves recovery is showed on T7-T12.
If SCI patients regain skin sensation on this level usually can lift the thigh up to the hip.
1-4. Inter–segmental spinal reflexes
Significance: These inter-segmental spinal reflexes are important for urgent treatment using acupuncture for SCI. This method can allow the nerve impulses to progress through the upper and lower lesion section of the white matter as well as release the wound and rapidly assists with recovery to the lesion in the spinal cord gray column.
Method: Inserting the needle into the skin receptors and muscles spindles while focusing on the vertebral column such as BL, GV and JIAJI points by using moderate needling and retention needles in the points.
The ‘opposition needle techniques’ can be start on BL41 meridian point down to BL54. In the case of lesion at T11 for example: the BL48-49-50 ACU points can be selected the tip of the needle is obliquely toward the spine or opposition the BL meridian QI flow direction and repetitive needling method is provided.
Method: the needle is inserted into the skin receptors and muscles spindles, the needle tip is obliquely opposite the meridian line and rapid and repetitive needling techniques is applies.
The nerve impulses may progress through the white column, ascend to the central motor nuclei via the descending tracts, and react to the motor neurons in grey column of spinal cord.
If needling into the points at BL11 down, the tip of the needle is following the meridian line allows the descending tracts work on spinal cord gray column activated the motor neurons function.
The point selection:
Where the vertebral column is damaged that level
Needle insertion is starts from the upper part of the vertebral column down to the below vertebrae.
Results: The treatment take times for recovery usually when needles sensation regain function at T12 level the patient can lift the legs up to the hip.
“““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““`
Back shu points
There are three sets of meridian points: Jiaji, GV and BL on the vertebral column in which are significance in treating SCI.
The damage vertebral column may involve two to three vertebrae, the ACU points surrounding the vertebral column such as GV, JIA-JI, and BL meridian points are selected. The inter-segmental spinal reflexes are important for urgent treatment applies acupuncture for SCI. This method can allow the nerve impulses to progress through the upper and lower lesion section of the white matter as well as release the obstructive wound and rapidly assists with recovery to the lesion in the cord.
The result is:
Repeat and intensive ACU treatments the skin sensation will regain; take about one to two months for a section of segmental of the cord recovery. ACU treatment should continuous following the same pattern further down to the next vertebral column.
The BL meridian points such as BL41 to BL54 is selected for strong repetitive needling method for fire the sensory neurons; the needle is inserted into the skin receptors and the muscle spindles and obliquely upward opposite the BL meridian line after needling gentle scratched the point upward show red in color.
This needle technique is applies for Debbie SCI initial T7 down to BL54 one year after ACU treatment her spine muscles is good enough supporting her for stand.
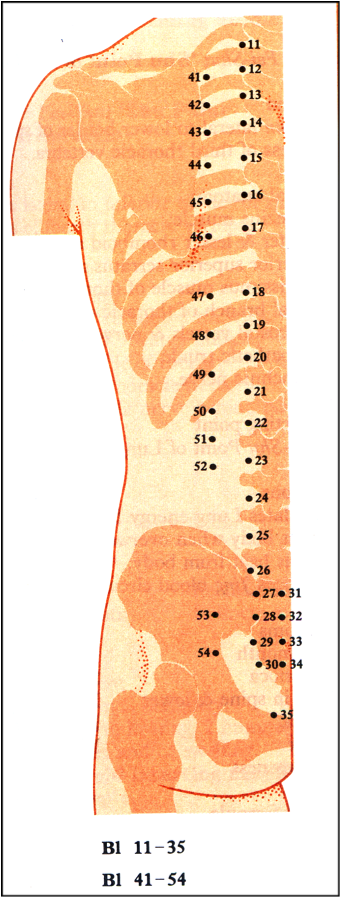
Five Shu Points
Five Shu Points originated in Ling Shu Jing, which is applies for treating upper or/and lower extremities illnesses. In treating SCI the result is significances.
The upper limbs five shu points:
Three Yin Meridians of Hand:
Lung – LU11, LU10, LU9, LU8, LU5
Pericardium – PC9, PC8, PC7, PC5, PC3
Heart – H9, H8, H7, H4, H3
Three Yang Meridians of Hand:
Large Intestine – LI1, LI2, LI3, LI5, LI11
Three Heaters – TH1, TH2, TH3, TH6, TH10
Small Intestine – SI1, SI2, SI3, SI5, SI8
The Five Shu Points of Lower Limbs
Three Yang Meridian points of foot
Stomach ST45 ST44 ST43 ST41 ST36
Gall Bladder GB44 GB43 GB41 GB38 GB34
Bladder BL67 BL66 BL65 BL60 BL40
Three Yin Meridians points of foot
Spleen SP1 SP2 SP3 SP5 SP9
Liver Liv1 Liv2 Liv3 Liv4 Liv8
Kidney K1 K2 K3 K7 K10
- Points on apex of fingers or toes:
Needle insertion:
The needle is rapidly inserted into the skin bring a droop of blood out of the point and no needle retention
Indication:
Sensitive point for strong stimulation
Improved lymphatic and blood circulation releases edema
SCI no feeling and reaction
Only when skin sensory neuron recovery show certain reaction and pain
- Jing-well points
Location: the point is located on the side of the corner of the finger or toenail
Method: the needle is rapidly inserted into the skin no needle retention
Sensation: For a normal patient needle insertion is painful, in the case of SCI it is no pain sensation only when the sensory neurons recovery shows pain.
- The Web
Location: on between two fingers or toes the neurovascular pathway
Needle insertion method:
Usually, the needle is inserted at the point located on the dorsal section of the web. If the needle is inserted at the palm side the reaction will be stronger. The needle is released the obstruction and stimulated the neurovascular pathway
- The phalangeal joint:
Two points are located on both sides of the phalangeal joint. The needle is inserted perpendicularly into the joint capsule. Needle insertion can also involve the tendons and interosseous muscle that attached to the joint.
The results: improves the joint tendon and muscles movement
The points on palm or plantar are sensitive for stimulation and need the needle retention
- The points on the wrists or ankles
There are tendons cross the wrist or ankle and the ligament stability the joint
For the case of SCI:
After SCI need to provided external support for stability the joint
Point selection: lower limbs
The points surrounding the ankle such as K2 and K3 BL60 BL62 GB40 ST41 SP5
The needles are target on the tendons ligaments and ankle joint
The foot the ankle and the tendons are significant in paraplegia legs movement
Method:
Repetitive needling method is following on the side of the tendons direction provided blood flowing and stimulation; after needling gentle scratching and passive movement.
Needles are retention in the ACU points for fifteen minutes.
Observation: focuses on the calculus tendon and gastrocnemius and soleus muscles reaction
- The muscles below the knee: HE sea points
The needle insertion methods:
Such as the needle is inserted at the point of GB34 the needle insertion is involved the peroneus longus and extensor digitorum longus and the point ST36 is involved the tibialis anterior a single individual muscle.
That is preferable makes a line cross GB34 and ST36 the peroneus longus extensor digitorum longus and tibialis anterior the points are 1 cm interval on the line. The needles are perpendicularly inserted into the skin and fascia of the muscles.
The flexor digitorum longus is coordinated with the extensor digitorum longus in which is the same as tibialis poterior is coordinated with tibialis anterior.
There are few ACU points on the line of tibialis anterior for example:
In general ST 36 is located on the tibialis anterior origin of the muscle and the ST40 seems located on terminate of the muscle and the tendon cross the leg to the base of metatarsal bone.
In needle inserted to the muscle that is preferred begin from the origin and the belly of the muscle and terminal to insertion of the muscle.
ACU treatment involved needle insertion, moxa, scratching, stretching and maintaining correct body postural position all in which is a system in treatment processes observation the illness finding and the treatment result.
ACU points, Brainstem and Central motor nuclei
In clinical ACU treatment without correctly managing of central motor nuclei cooperate with lower motor neurons functional communication: the paralyzed patients particularly the Quadriplegia patient difficult achieve proper muscles coordinated movement and voluntary movement.
Pons
The pons lies between the medulla oblongata and the midbrain. It contains tracts that carry signals from the cerebrum to the medulla and to the cerebellum as well as tracts that carry sensory signals to the thalamus.
Twelve pairs of cranial nerves nuclei are involved with the pons. These include most of the sensory organs, which include vision, hearing, balance, body posture, smell, swallow and speech. In particular, the CN10 -Vagus nerve, which is involved the internal organ functions such as bowel movements, urination and sexuality, that is lost in the SCI patient.
Acupuncture treatment requires needling to the pathways for example: where the scalp of the foramen is located that is the Vagus nerve exits to the skull and passes through the neck to the abdomen.
Inserting the needles into the skin and muscles of the face and head at the scalp points strengthens the function of the pons has great valuable than releasing the symptoms. Especially cranial nerves of CN1, CN3, CN8, CN10, CN11 and CN12 are more involved in SCI.
ACU and CN10 for example:
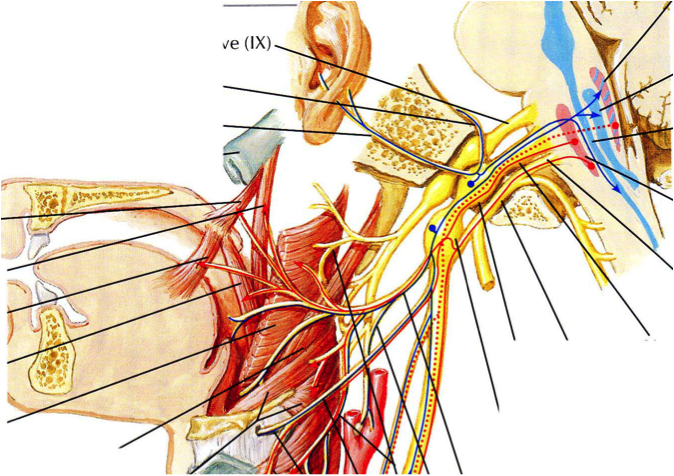
Vagus nerve—CNX
General consideration:
The CN X is extends through the jugular foramen, then passing into the carotid sheath between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein down below the head, to the neck, chest and abdomen, where it contributes to the innervations of the viscera.
The point of neuropath:
Jugular foramen—point behind the ear TH17 TH18
Carotid sheath—point is on the side of sternocleidomastoid LI18 ST9
The head injury at temporal ear region or the neck trauma in SCI may cause damage to Cranial nerves especially involved to CNX, CNXI and CNXII.
Vestibular tract also involved the head neck and eyes need balance posture.
Medulla oblongata
Spinal cord initiated medulla oblongata at the base of skull (foramen magnum) the cervical vertebra C1 down to the first lumbar vertebra, lesion to any segmental of the cord cause SCI and medulla oblongata is located on a high-risk region for SCI and that is the key point of acupuncture when treating SCI.
Trauma in the pyramidal tracts can cause severe SCI. If the sensation cannot get through the olive medulla, then the cortico-spinal tracts cannot send the motor signal to the spinal cord and thus motor movement is impaired. The urgent treatment of SCI in this region is of significant importance.
According to ACU clinical treatment perception the point selection are focused on where the damages parts that is the main issue point.
The points on the back of skull and scalp:
Trapezius attached to skull—GB 20, BL10
Mastoid process—sternocleidomastiod TH17
Jugular foramen—GB12
The points on the neck
Mandible: neck angle oblique line and incisive fossa of mandible and at the lateral surface of coronoid process-St5-6-7, St10-11-12-13
Clavicle: sterno-cleido-mastoid attachment, pectoralis major, and clavicle fossa- LU1-2
Hyoid-CV22-23
Temporalst-GB8
